
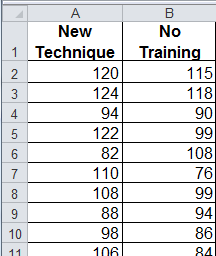
The following Excel formula can be used to calculate the two-tailed probability that.
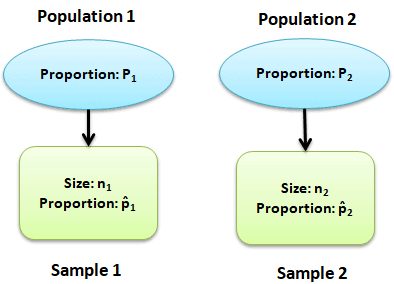
There are 2 ways to compute the two sample Z test of proportions i.e pooled or unpooled. Remarks If array is empty, Z.TEST returns the N/A error value. Two Sample Z Test of Proportions Variations The difference between population proportions is less than hypothesized difference (left -tailed).The difference between population proportions is greater than hypothesized difference (right-tailed).Alternative hypothesis: The difference between population proportions is not equal to hypothesized difference (two -tailed).Null hypothesis: The difference between population proportions is equal to hypothesized difference.Hypothesis of two sample Z proportion test Test results are accurate when np and n(1-p) are greater than 5.Both populations follow a binomial distribution.The data are simple random values from both the populations.Assumptions of the Two Sample Z Proportion Hypothesis Tests Use two sample z test of proportion for large sample size and Fisher exact probability test is an excellent non-parametric test for small sample sizes. The purpose of two sample Z test is to compare the random samples of two populations. The Z-value is 3.648 which is above the critical value of 2.5758 (two tailed test), thus there is a significant difference between the soils.For example, compare the proportion of men baseball players who are right-handed to the proportion of women baseball players who are right-handed. Now when you have the variances you use the formula for Z-test two independent samples or you can use the calculator provided.
Standard deviations for each sample thus you need to take the square of the standar deviations to find the variances: When performing a Z-test on two independent samples you want to sum the variances of the means and then take the square root to find the standard deviation of variance sum. The soils appear to differ with respect to average shear strength, at the 1% significance level? Sample means when you want to see if there is any different between the means of two normally distributed samples.Įxample, Shear strength measurements derived from unconfined compression tests for two types of soils gave the results shown in the following table (measurements in tons per square foot). Calculate statistical significance and the Power of your A/B-test.
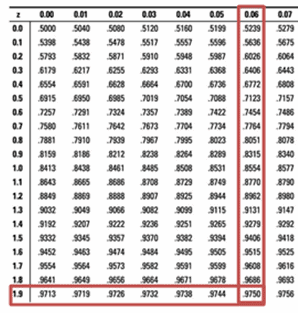
For this test: Ho : p 0.2 Ha P / 0. When do you use Z-test two independent sample means?Ī Z-test assumes the data is normally distributed which according to the central limit theorem is when the sample size is large, usually when n > 30. one-proportlon hypothesis test at the 5 significance level to test whether the true proportion Of weekday movle-goers who g0 most frequently on Fridays different from 20.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
